. 07/10/2024 1:22 PM
Choosing civil services as a career, particularly roles like IAS, IPS, and IFS, offers a unique opportunity to make a significant impact on the nation while enjoying authority, respect, and job security. Unlike private sector jobs, civil services allow individuals to work directly for the public good, driving positive change on a national scale. Moreover, IAS officers play a crucial role in policy-making, tackling pressing social issues and representing India on international platforms. For those passionate about making a difference, civil services provide a fulfilling and stable career path that empowers individuals to effect real change in society.
To be selected for these coveted services, candidates must appear for the Civil Services Exam (CSE) conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) and pass a three-phase selection process: the Civil Services Preliminary Exam (Prelims), the Civil Services (Main) Examination (Mains), and the Personality Test (Interview).
Candidates are required to apply online using the official UPSC website: www.upsconline.nic.in. The online application form consists of two stages: Part-I and Part-II, as per the instructions available on the aforementioned website.
Candidates must pay a fee of Rs. 100 (Rupees One Hundred only), except for SC/ST/Female/Persons with Benchmark Disabilities, who are exempted from payment. Payment can be made either by depositing money in any branch of the State Bank of India by cash, using the net banking facility of the State Bank of India, or by using any Visa/Master/RuPay credit/debit card.
Before starting to fill out the online application form, candidates must have their photograph and signature scanned in jpg format, ensuring that each file does not exceed 40 KB and is not less than 3 KB in size for the photograph and 1 KB for the signature.
Applicants should avoid submitting multiple applications. In the case of multiple applications, only the application with the higher Registration ID will be considered by the Commission.
Candidates must ensure that they provide valid and active email IDs while filling out their application form, as the Commission may use electronic communication to contact them at different stages of the examination process.
The Civil Services Examination consists of two successive stages:
Civil Services (Preliminary) Examination (Objective type) for the selection of candidates for the Main Examination.
Civil Services (Main) Examination (Written and Interview) for the selection of candidates for various services and posts.
Candidates who qualify for the Civil Services (Main) Examination must submit a Detailed Application Form (DAF).
The Civil Services (Preliminary) Examination comprises two papers of 200 marks each: General Studies Paper I and General Studies Paper II. GS Paper II (also known as the Civil Services Aptitude Test or CSAT) is qualifying in nature; a candidate needs to secure only 33% marks in this paper.
This stage consists of objective type (Multiple Choice Questions) assessments. Marks obtained in this stage are counted only for determining merit in the preliminary examination and not for final selection. Clearing the Prelims makes a candidate eligible for the next stage of the exam.
The Civil Services (Main) Examination is the written stage of the examination, consisting of nine papers. The marks of only seven papers are counted toward the final merit list; candidates must secure minimum qualifying marks in the remaining two papers as decided by UPSC each year. The question papers for the Mains examination are of a conventional (essay) type.
The Civil Services Personality Test consists of a board of members assessing the candidate’s personality. Candidates are asked questions on matters of general interest. The objective of the interview is to assess the personal suitability of the candidate for a career in public service, judged by a board of competent and unbiased observers. The test is intended to evaluate the mental caliber of a candidate.
The final rank of a candidate in the merit list depends solely on the marks scored in the second stage, i.e., the written examination and the interview.
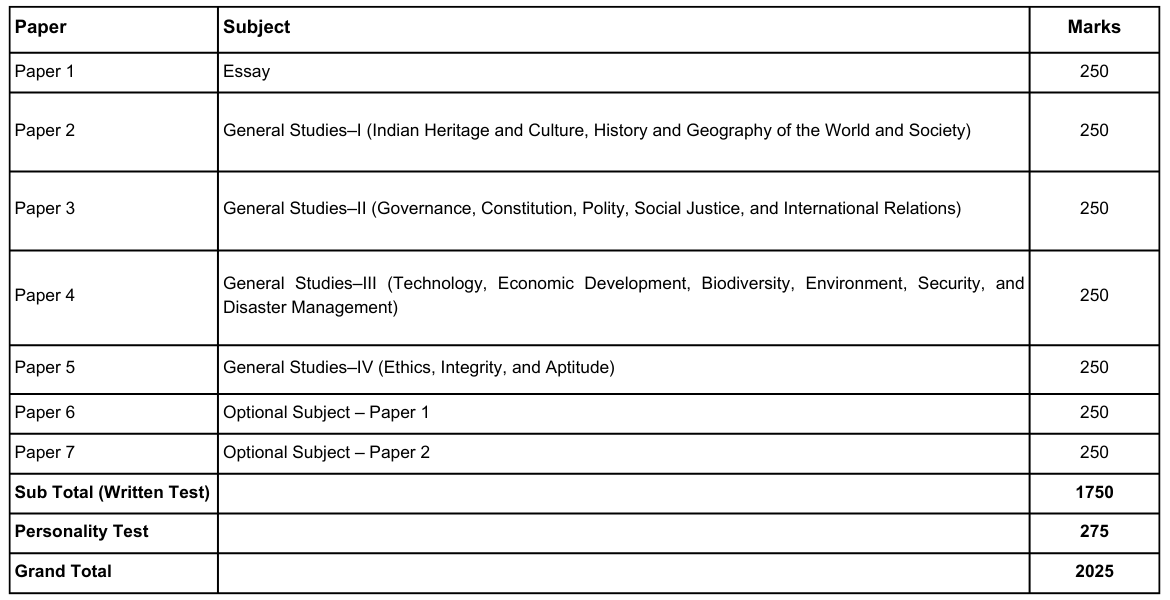
Two qualifying papers are:
Paper-A: One of the Indian languages selected by the candidate from the languages included in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution (300 Marks).
Paper-B: English (300 Marks).
For the IAS and IPS, a candidate must be a citizen of India. For other services, a candidate must either be a citizen of India or a citizen of another country, eligible after meeting certain special conditions.
Candidates must have attained the age of 21 years and must not have exceeded the age of 32 years on the 1st of August of the examination year. The upper age limit is relaxable by a maximum of 5 years for SC/ST candidates and 3 years for OBC candidates. Age relaxation is also applicable for ex-defense personnel and candidates with certain disabilities.
Candidates must hold a university degree or possess an equivalent qualification to appear for the Civil Services Examination. Candidates who have appeared in the final year of their degree examination, as well as those intending to appear for such a qualifying examination, are also eligible to apply for the Preliminary Examination. However, they must provide proof of passing the requisite examination before appearing for the Civil Services (Main) Examination.
A candidate who has been appointed as an IAS or IFS officer in an earlier examination and continues to be a member of that service will not be eligible to compete in this examination. Additionally, a candidate appointed to the Indian Police Service will not be eligible to opt for the Indian Police Service in the next examination.
Indian P&T Accounts & Finance Service
Indian Audit and Accounts Service
Indian Revenue Service (Customs and Central Excise)
Indian Defence Accounts Service
Indian Revenue Service (I.T.)
Indian Ordnance Factories Service (Assistant Works Manager, Administration)
Indian Postal Service
Indian Civil Accounts Service
Indian Railway Traffic Service
Indian Railway Accounts Service
Indian Railway Personnel Service
Indian Railway Protection Force (Assistant Security Commissioner)
Indian Defence Estates Service
Indian Information Service (Junior Grade)
Indian Trade Service, Group 'A' (Gr. III)
Indian Corporate Law Service
Armed Forces Headquarters Civil Service (Section Officer's Grade)
Delhi, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Daman & Diu, and Dadra & Nagar Haveli Civil Service (DANICS)
Delhi, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Daman & Diu, and Dadra & Nagar Haveli Police Service (DANIPS)
Pondicherry Civil Service
Pondicherry Police Service
Agriculture
Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science
Anthropology
Botany
Chemistry
Civil Engineering
Commerce and Accountancy
Economics
Electrical Engineering
Geography
Geology
History
Law
Management
Mathematics
Mechanical Engineering
Medical Science
Philosophy
Physics
Political Science and International Relations
Psychology
Public Administration
Sociology
Statistics
Zoology
Literature of any one of the following languages:
Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, and English.